What is the Plastic Injection Moulding Process and How Does it Work
The plastic injection moulding process is a pivotal technique in modern manufacturing, particularly for producing a wide range of plastic products. This method involves injecting molten plastic resin into a custom-designed mould, where it solidifies into the desired shape. As industries continue to evolve, understanding the intricacies of the plastic injection moulding process becomes crucial for engineers, designers, and manufacturers alike. This process not only optimizes efficiency and reduces waste but also allows for high-volume production with remarkable precision.
In this article, we will delve into the step-by-step procedure of the plastic injection moulding process, exploring its key stages, advantages, and potential applications. From the initial stages of material selection and heating to the final steps of cooling and ejection, each phase plays a crucial role in ensuring quality and consistency in the finished product. By grasping these concepts, readers will gain insights into how this innovative manufacturing technique shapes the products we use daily, while also highlighting the technological advancements that continue to enhance its capabilities.
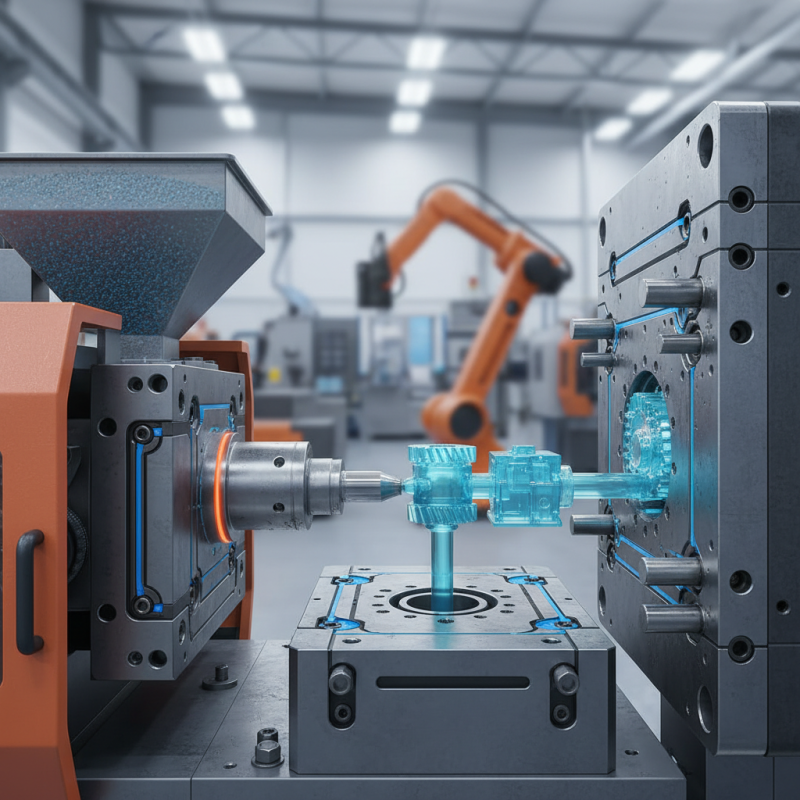

Overview of Plastic Injection Moulding Process

The plastic injection moulding process is a highly efficient and versatile manufacturing technique used to create a wide range of plastic parts. The process begins with the heating of plastic materials until they reach a molten state. This molten plastic is then injected into a mould cavity under high pressure. The mould, typically made from metal, is designed to shape the plastic into the desired form. Once the plastic cools and solidifies, the mould opens, and the finished piece is ejected.
One of the primary advantages of plastic injection moulding is its ability to produce complex geometries with high precision and repeatability. This makes it ideal for mass production, as multiple identical parts can be manufactured quickly. Additionally, the process allows for the incorporation of various additives and colorants into the plastic, providing flexibility for product customization. With advancements in technology, injection moulding continues to improve in efficiency and capability, making it a popular choice across various industries, including automotive, consumer goods, and electronics.
Key Components of Injection Moulding Machinery
The injection moulding process is a highly efficient method for producing plastic parts, and its machinery consists of several key components that contribute to its effectiveness. At the heart of the system is the injection unit, which is responsible for melting the plastic granules and injecting them into the mould. This unit typically includes a hopper for feeding the material, a reciprocating screw or plunger for melting and transporting it, and a heated barrel that maintains the proper temperature for optimal flow. According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the global injection moulding machine market is expected to reach USD 8.6 billion by 2025, highlighting the growing demand for this manufacturing technology.
Another crucial component is the clamping unit, which holds the mould in place during the injection process. The clamping process must exert a considerable force to securely close the mould, which can range from as low as 20 tons to over 6,000 tons, depending on the size and complexity of the part being produced. This unit also has mechanisms to open and eject the part once it has cooled and solidified. The efficiency of the clamping unit not only influences cycle time—averaging around 15 to 30 seconds—but also impacts the overall quality of the finished product. Industry analysts suggest that advancements in hydraulic and electric clamping technologies are driving growth and efficiency within this segment of the injection moulding market.
Step-by-Step Procedure of Plastic Injection Moulding
The plastic injection moulding process is a highly efficient and versatile manufacturing method used to create a wide variety of plastic products. The procedure begins with the selection of raw plastic materials, which are typically in pellet form. These pellets are then fed into a heated barrel where they are melted and mixed to achieve a uniform consistency. Once the plastic reaches the appropriate temperature, it is injected under high pressure into a pre-designed mould cavity, where it cools and solidifies to take the desired shape.
After the plastic has cooled, the mould is opened, and the finished part is ejected. This step is crucial as it ensures that the product is removed without damage. Depending on the complexity of the design, additional processes such as trimming or surface finishing may be required after ejection.
Tips for achieving optimal results in plastic injection moulding include maintaining consistent temperature and pressure during the injection phase, as fluctuations can lead to defects in the final product. Additionally, it's essential to conduct regular maintenance on the moulding equipment to prevent wear and tear, which can negatively impact both quality and efficiency. Finally, proper design considerations such as draft angles and rib placements can significantly enhance the manufacturability and functionality of the final products.
Plastic Injection Moulding Process Steps Frequency
Factors Affecting Injection Moulding Quality and Efficiency
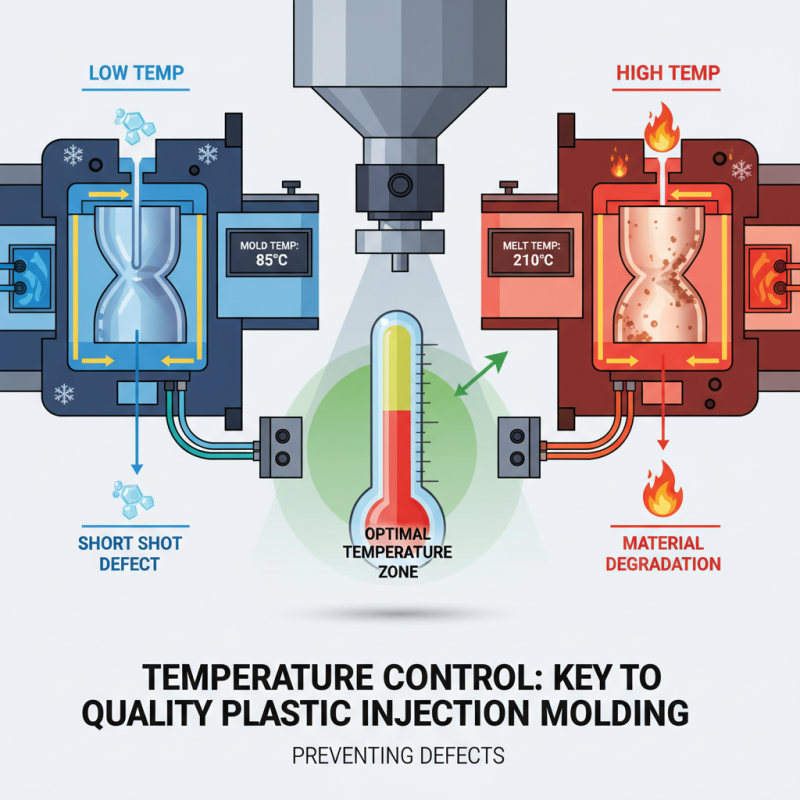
The quality and efficiency of the plastic injection moulding process are influenced by several critical factors. One of the primary elements is the temperature of both the injection mould and the molten plastic material. If the mould temperature is too low, it may lead to incomplete filling and result in defects like short shots. Conversely, an excessively high temperature can cause the material to degrade, impacting the final product's strength and appearance. Therefore, carefully controlling the temperature is essential to achieving optimal moulding results.
Another significant factor is the injection speed, which affects the fill time and pressure within the mould. A higher injection speed can reduce cycle time but may introduce air traps or result in increased stress on the part, leading to warping or dimensional inaccuracies. Additionally, the choice of materials plays a crucial role—different plastics have varying flow properties and cooling characteristics that can further complicate the moulding process. By understanding and balancing these factors, manufacturers can enhance both the quality and efficiency of their injection moulding operations.
Applications and Advantages of Plastic Injection Moulding
Plastic injection moulding is a widely used manufacturing process known for its versatility and efficiency in producing plastic parts. One of the primary applications of this technique is in the automotive industry, where it is utilized to create intricate components such as dashboard elements, housings, and small fixtures. Additionally, the consumer goods sector relies on injection moulding to manufacture everything from kitchen utensils to toys, enabling the mass production of durable and aesthetically pleasing products.
The advantages of plastic injection moulding are significant. It allows for high-volume production, making it cost-effective for manufacturers, especially when producing large quantities of identical items. The process also offers a high degree of precision, ensuring that parts are made to exact specifications, reducing the need for extensive post-production machining. Moreover, with the ability to use a wide range of materials, including thermoplastics and thermosetting polymers, manufacturers can select materials that best suit their application's requirements, whether that be strength, flexibility, or resistance to environmental factors. This flexibility, combined with design freedom and quick turnaround times, makes plastic injection moulding a preferred choice across multiple industries.
Related Posts
-

Innovative Molding Tools for Streamlined Manufacturing Processes
-

Understanding the Process: How Injection Molding Molds Shape Our Daily Products
-

What is Plastic Mold Injection Machine? A Comprehensive Guide to Its Types and Applications
-

Top 10 Benefits of Mold Injection for Effective Product Manufacturing
-
Discover the Best Union Tool Products: 2025 Top Digital Types You Need
-
How to Choose the Right Injection Molding Tooling for Your Project
